
 |
||||
|
||||
Technologies on Display
G2 - Innovative Applications of Spoken Language Technologies
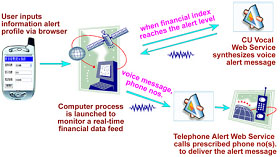 (1)
CU VOCAL: A Cantonese Text-to-speech Synthesizer
(1)
CU VOCAL: A Cantonese Text-to-speech Synthesizer
CU VOCAL is a Cantonese text-to-speech (TTS) engine that generates highly
natural and intelligible synthetic speech based on input Chinese text. It
enables dynamic information delivery via a spoken presentation in Cantonese.
CU VOCAL adopts a syllable-based concatenative approach that considers both
coarticulatory and tonal contexts. A sophisticated language processor is
also developed for word segmentation, appropriate concept verbalization,
named entities identification, automatic disambiguation among multiple
pronunciations in Chinese as well as mixed language (Chinese and English)
handling.
Unique Features
- Highly natural and intelligible speech output
- Technology applicable to Cantonese and Putonghua
- Speech quality optimizable for specific domains
Applications
-
 CU
VOCAL Web Service:
CU
VOCAL Web Service:
The First Chinese Text-to-speech Web Service
- Voice-enabled applications and multimedia
messaging over the Web
- Highly interoperable with other Web services
(e.g. message multicasting Web service)
- No need for local installation and maintenance
- Transparent TTS engine upgrades - Client-based CU VOCAL:
The First Cantonese SAPI Compatible Engine
- Easily invoked by Windows-based applications
- Microsoft SAPI 5.1 compatible
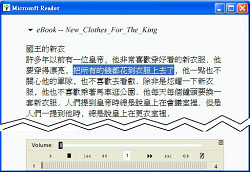
- Potential applications include story reading (eBook),
webpage/screen reader and announcement systems
Website
http://www.se.cuhk.edu.hk/cuvocal
(2) Audio Search Engine
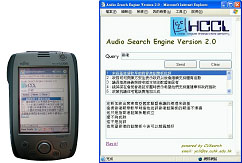 This
project enables cross-media information retrieval whereby users can use
textual or spoken queries to retrieve relevant video and audio documents. We
integrate Chinese speech recognition with information retrieval technologies
to develop the first system for Cantonese spoken document retrieval. Our
novel approach indexes and retrieves spoken audio documents in real time.
This
project enables cross-media information retrieval whereby users can use
textual or spoken queries to retrieve relevant video and audio documents. We
integrate Chinese speech recognition with information retrieval technologies
to develop the first system for Cantonese spoken document retrieval. Our
novel approach indexes and retrieves spoken audio documents in real time.
Unique Features
- First Cantonese speech retrieval system
- Novel approach uniquely suitable for monosyllabic languages (e.g. Chinese)
- Use of subword units circumvents the segmentation ambiguity in Chinese
- Extensible to cross-language speech retrieval systems
(e.g. using English queries to retrieve Chinese documents)
Applications
- Multimedia Information Search on Desktop and
Handheld Computers
- Textual queries may be input by typing or handwriting recognition
- Spoken queries are recognized by the CUHK Cantonese speech recognition engine (CURSBB)
Websites
(desktop)
http://www.se.cuhk.edu.hk/hccl/audiosearch
(handheld)
http://www.se.cuhk.edu.hk/hccl/mobileaudiosearch
Principal Investigator
Professor Helen Meng
Department of Systems Engineering and Engineering Management
¡@

